Os Trigonum Syndrome Mri
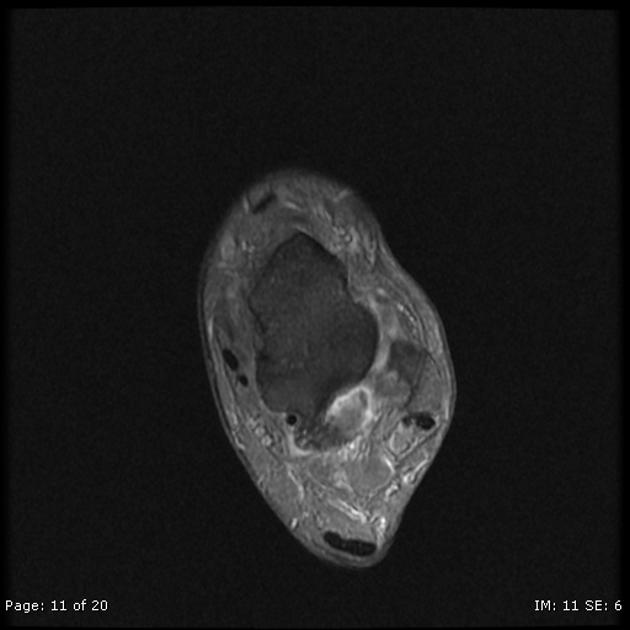
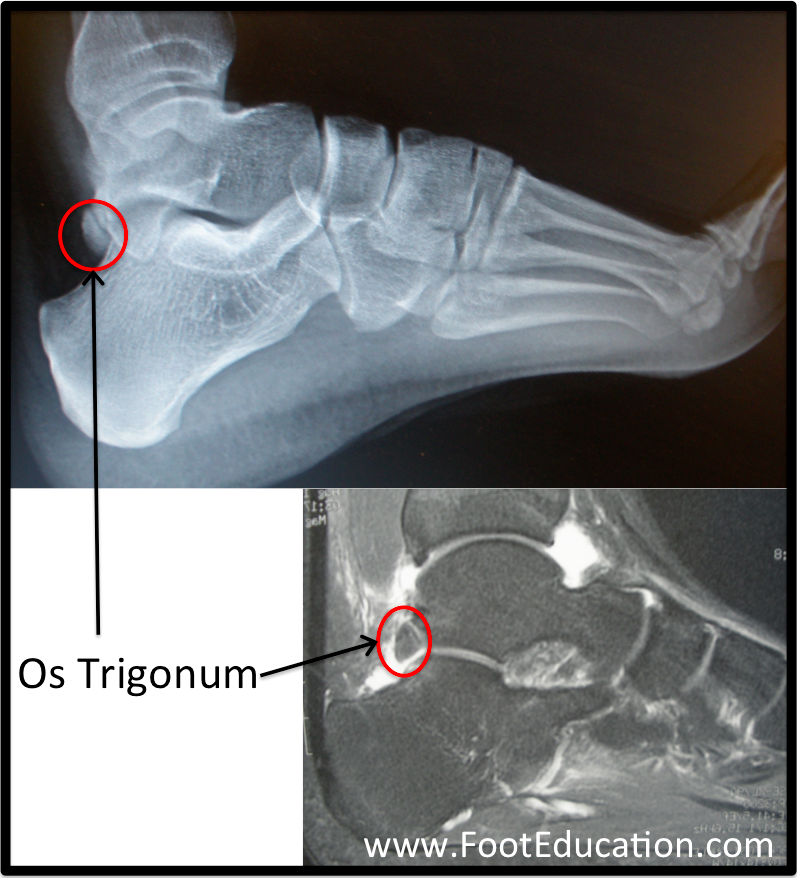
Os trigonum syndrome mri. An x-ray will show a small accessory bone with smooth edges distinguishes it from a fracture of the talus. Diffuse patchy-marrow edema can appear throughout the hind foot. Os trigonum syndrome is the result of an overuse injury of the posterior ankle caused by repetitive plantar flexion stress.
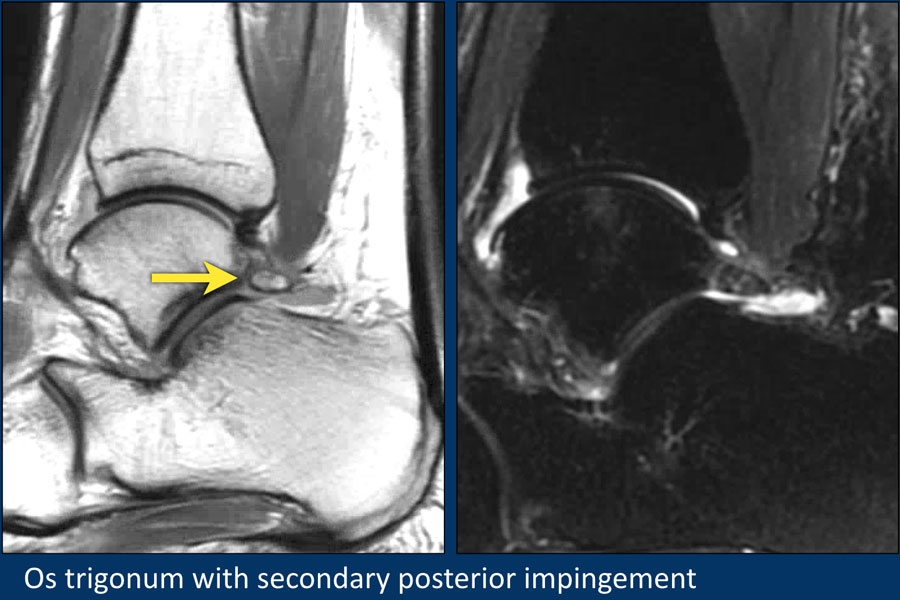
Ankle Posterior Impingement Os Trigonum Syndrome Posterior ankle impingement is an uncommon problem that results from activities that utilize excessive pointing of the toes or straightening of the ankle most commonly dancing and ballet. 38 Other common sites of edema include the posterior talus 40 and the posterior calcaneum 24. Os trigonum syndrome is included within the broader category of posterior ankle impingement syndrome.
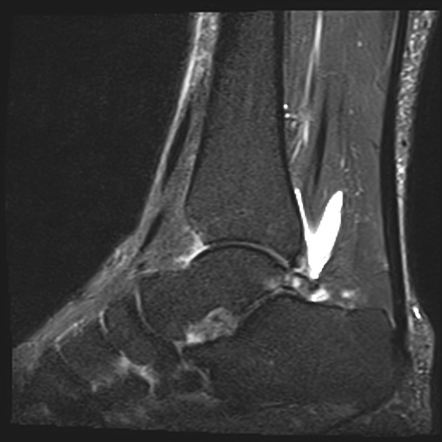
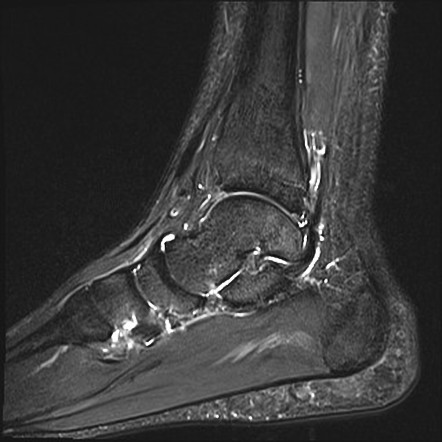
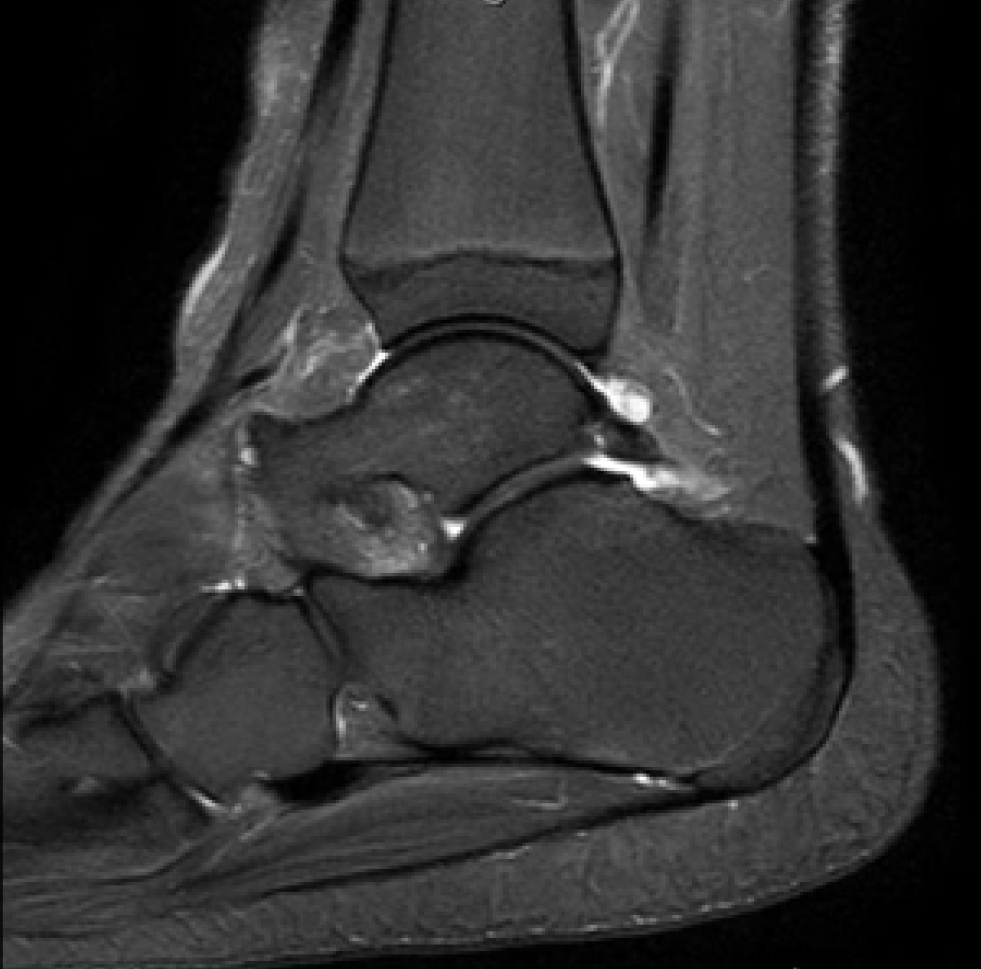
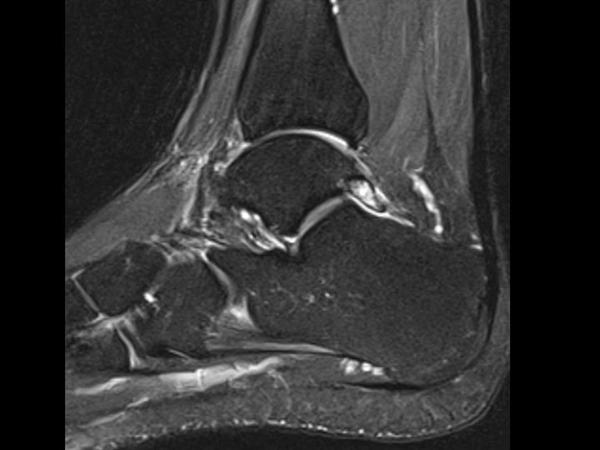
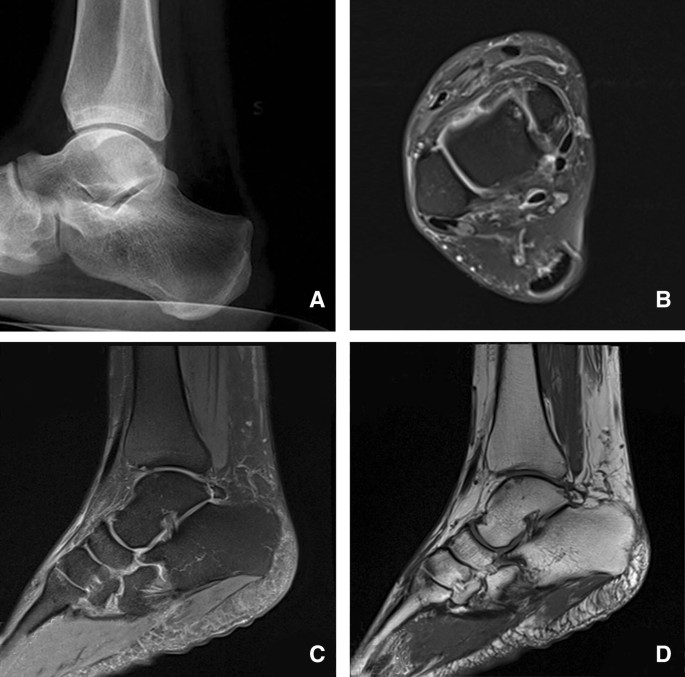
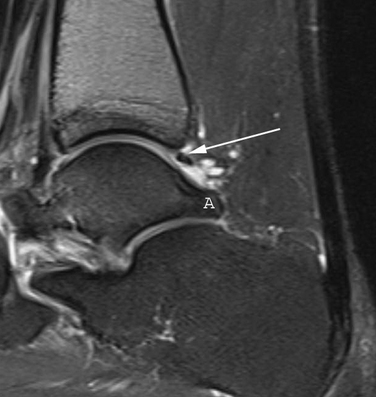
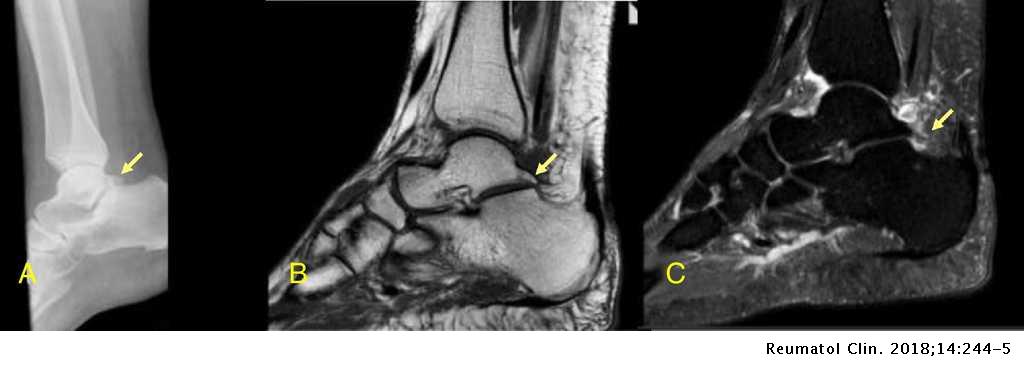
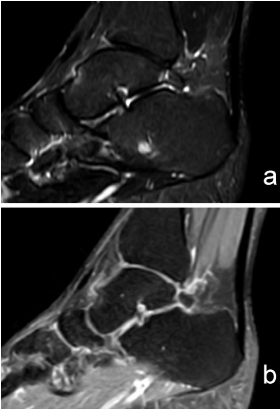
Os trigonum are a common finding and are usually asymptomatic - in this case however there is edema affecting the os trigonum and its synchondrosis. For the person who has an os trigonum pointing the toes downward can result in a nutcracker injury. Diagnosis of os trigonum syndrome begins with a thorough history and examination of the foot and ankle.
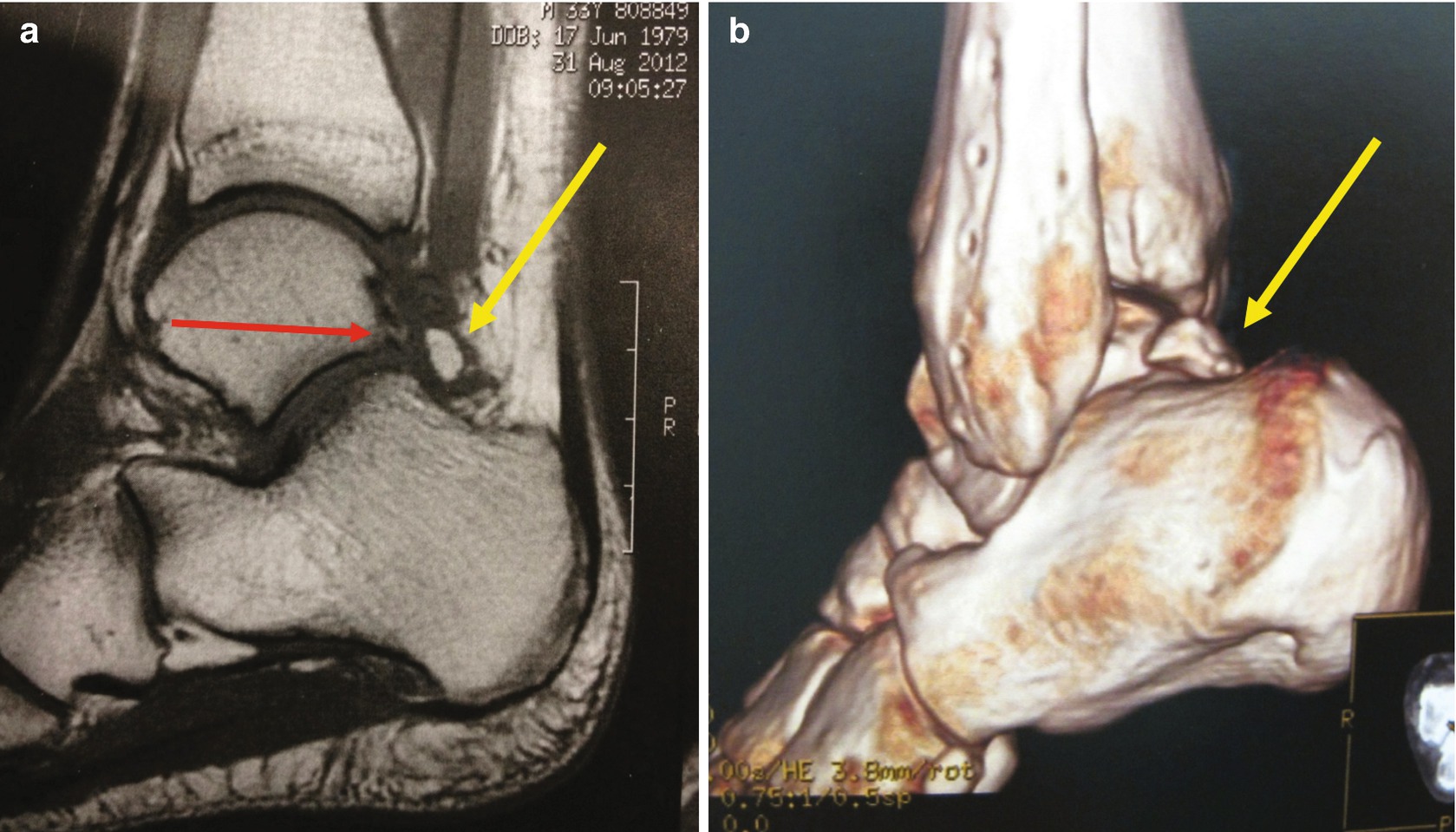
The syndrome is also frequently caused by repeated downward pointing of the toes which is common among ballet dancers soccer players and other athletes. Os trigonum syndrome is usually triggered by an injury such as an ankle sprain. 8 MR imaging can reveal fracture through the os trigonum or fluid in synchondrosis indicating os trigonum.
In conclusion for the differential diagnosis of hindfoot pain in clinically suspected os trigonum syndrome MRI appears to be the technique of choice after conventional radiography thanks to its noninvasiveness multiplanarity and high spatial and contrast resolution. The condition may also be referred to as posterior ankle impingement. Bone contusions of the lateral talar tubercle and os trigonum are prevalent MR imaging findings of PAI syndrome.
Os trigonum syndrome is a stress injury of the synchondrosis that is most commonly associated with acute or chronic repetitive hyperplantarflexion and has been frequently described in ballet dancers 32 35 and soccer players 36. Pain can be caused by disruption of the cartilaginous synchondrosis between the os trigonum and the lateral talar tubercle as a result of repetitive microtrauma and chronic inflammation. Os trigonum syndrome is generally considered synonymous with posterior ankle impingement syndrome although the latter can occur without the presence of an os trigonum many of the other features of soft tissue inflammation are the same.
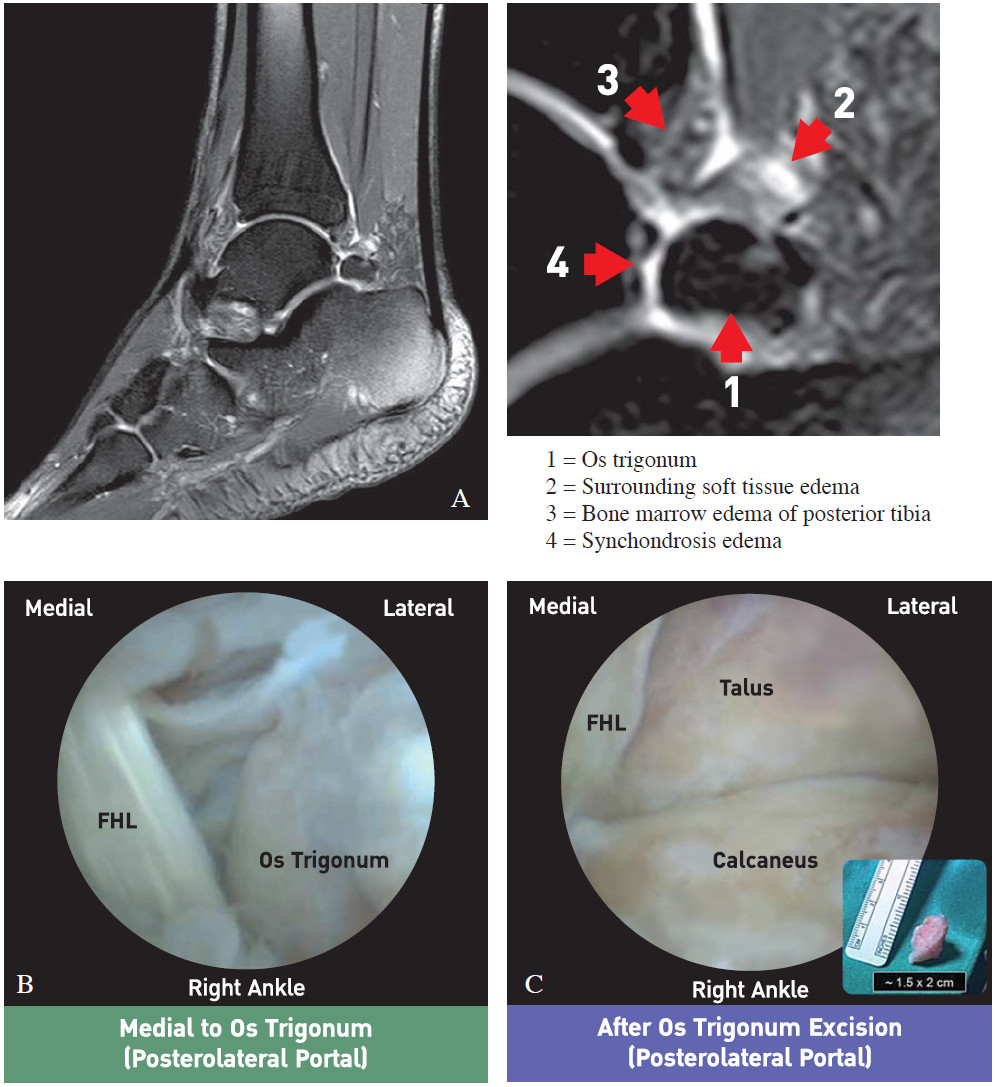
MR imaging demonstrates bone marrow edema within the os trigonum and at synchondrosis with the posterior talar tubercle a reliable sign of PAI syndrome. To confirm the diagnosis x-rays or MRI are usually ordered.
MR imaging clearly depicts the osseous and soft-tissue abnormalities associated with PAI syndrome and is useful in the assessment of this condition.
8 MR imaging can reveal fracture through the os trigonum or fluid in synchondrosis indicating os trigonum. Posterior refers to the back side of the ankle. To confirm the diagnosis x-rays or MRI are usually ordered. An x-ray will show a small accessory bone with smooth edges distinguishes it from a fracture of the talus. Os trigonum syndrome is included within the broader category of posterior ankle impingement syndrome. Diffuse patchy-marrow edema can appear throughout the hind foot. 8 MR imaging can reveal fracture through the os trigonum or fluid in synchondrosis indicating os trigonum. MR imaging demonstrates bone marrow edema within the os trigonum and at synchondrosis with the posterior talar tubercle a reliable sign of PAI syndrome. Os trigonum syndrome is the result of an overuse injury of the posterior ankle caused by repetitive plantar flexion stress.
It is predominantly seen in ballet dancers and soccer players and is primarily a clinical diagnosis of exacerbated posterior ankle pain while dancing on pointe or. Os trigonum syndrome is included within the broader category of posterior ankle impingement syndrome. MR imaging clearly depicts the osseous and soft-tissue abnormalities associated with PAI syndrome and is useful in the assessment of this condition. Ankle Posterior Impingement Os Trigonum Syndrome Posterior ankle impingement is an uncommon problem that results from activities that utilize excessive pointing of the toes or straightening of the ankle most commonly dancing and ballet. It is predominantly seen in ballet dancers and soccer players and is primarily a clinical diagnosis of exacerbated posterior ankle pain while dancing on pointe or. Os Trigonum Syndrome is a painful condition located on the back of the ankle that arises from an extra bone that sometimes develops from the back of the ankle bone talus. Os trigonum syndrome is the result of an overuse injury of the posterior ankle caused by repetitive plantar flexion stress.































Post a Comment for "Os Trigonum Syndrome Mri"