Connective Tissue Disease Lungs
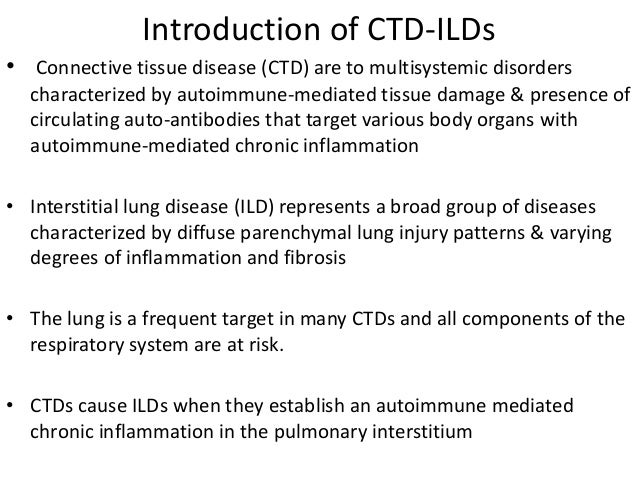
Connective tissue disease lungs. Auto means self and immune refers to your immune system. It can have multiple manifestations. Connective tissue diseases encompass a wide range of heterogeneous disorders characterised by immune-mediated chronic inflammation often leading to tissue damage collagen deposition and possible loss of function of the target organ.
Pulmonary manifestations of mixed connective tissue disease can be seen in a wide range 20-85 of those of mixed connective tissue disease. Introduction to connective tissue diseases. More commonly described features include.
Patients with mixed connective tissue disease MCTD exhibit clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus SLE progressive systemic sclerosis or scleroderma PSS and polymyositis-dermatomyositis PM-DM. Symptoms can include inflammation of the lining that covers the lungs and the inside of the chest difficulty breathing or pulmonary hypertension. In their sera is an unusually high titer of a circulating antinuclear antibody with specificity for a nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigen.
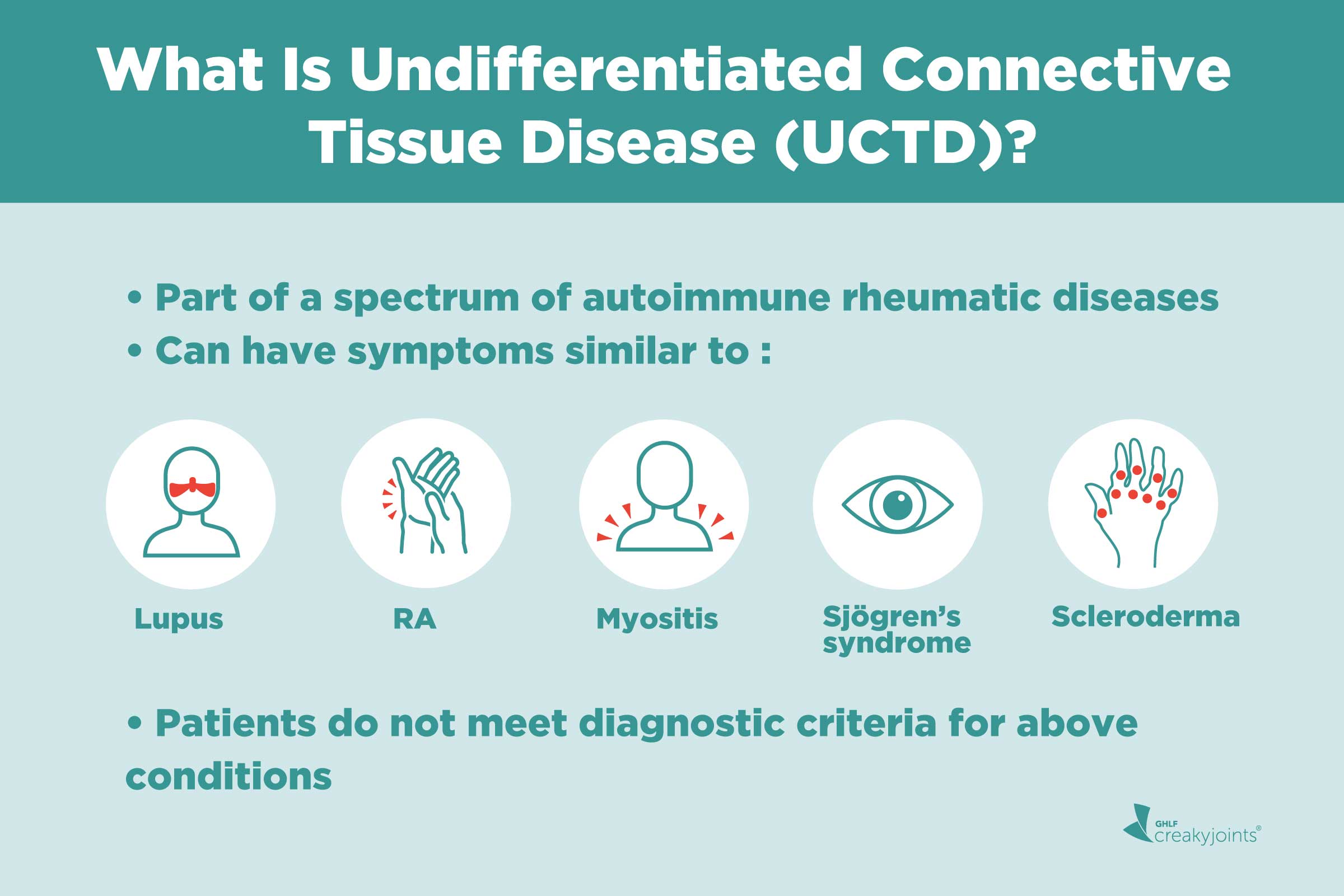
Lupus scleroderma and myositis. In autoimmune disease the bodys immune system can attack its own organs causing inflammation and injury. Mixed connective tissue disease.
Connective tissue disease associated with interstitial lung disease or CT-ILD is a lung condition that affects a small number of patients with a connective tissue disease. In this systemic disorder immune cells attack and inflame the membrane around joints. People with MCTD have symptoms and features of all three conditions either at the same time or over a period of time.
On the other hand mixed connective tissue disease MCTD is a mixture or overlap of three different autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Connective tissue diseases CTDs cause a myriad of pulmonary complications including bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis pleuritis and pulmonary hypertension. Examples of connective tissue diseases also known as rheumatologic collagen vascular or autoimmune diseases include scleroderma rheumatoid arthritis Sjogrens syndrome systemic lupus erythematosus polymyositis.
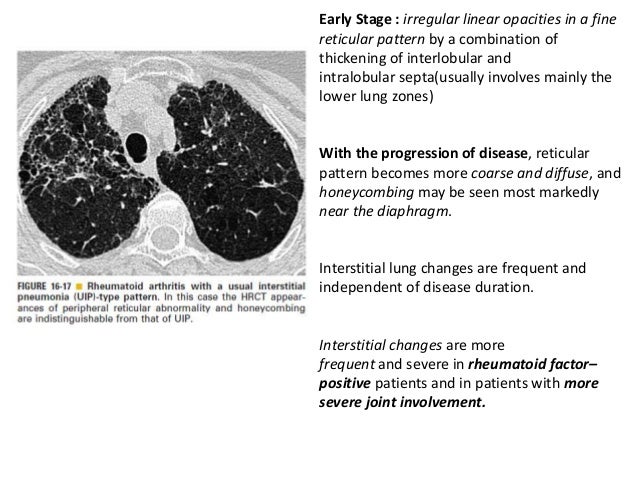
It also can affect the heart lungs and eyes. Early Stage.
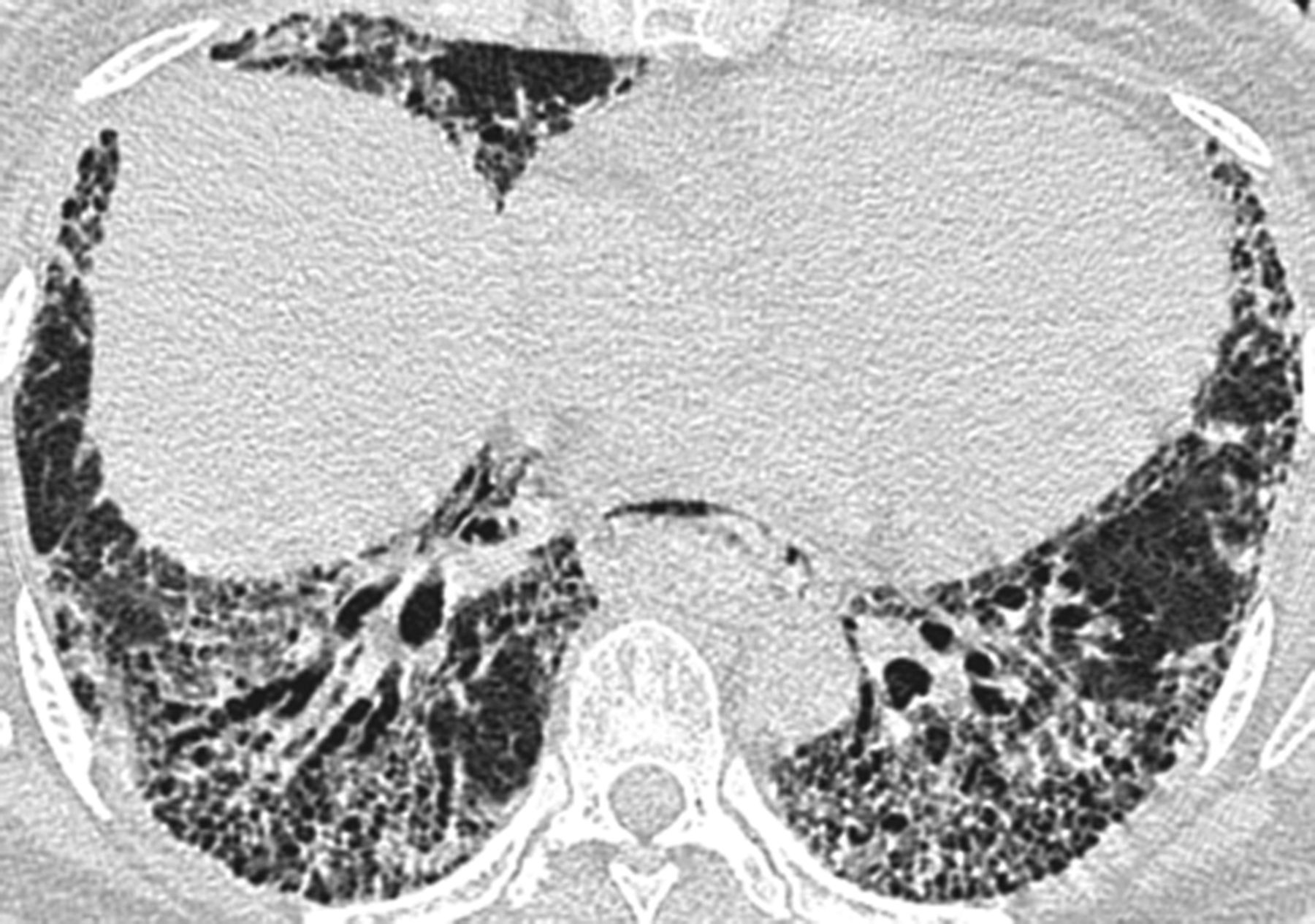
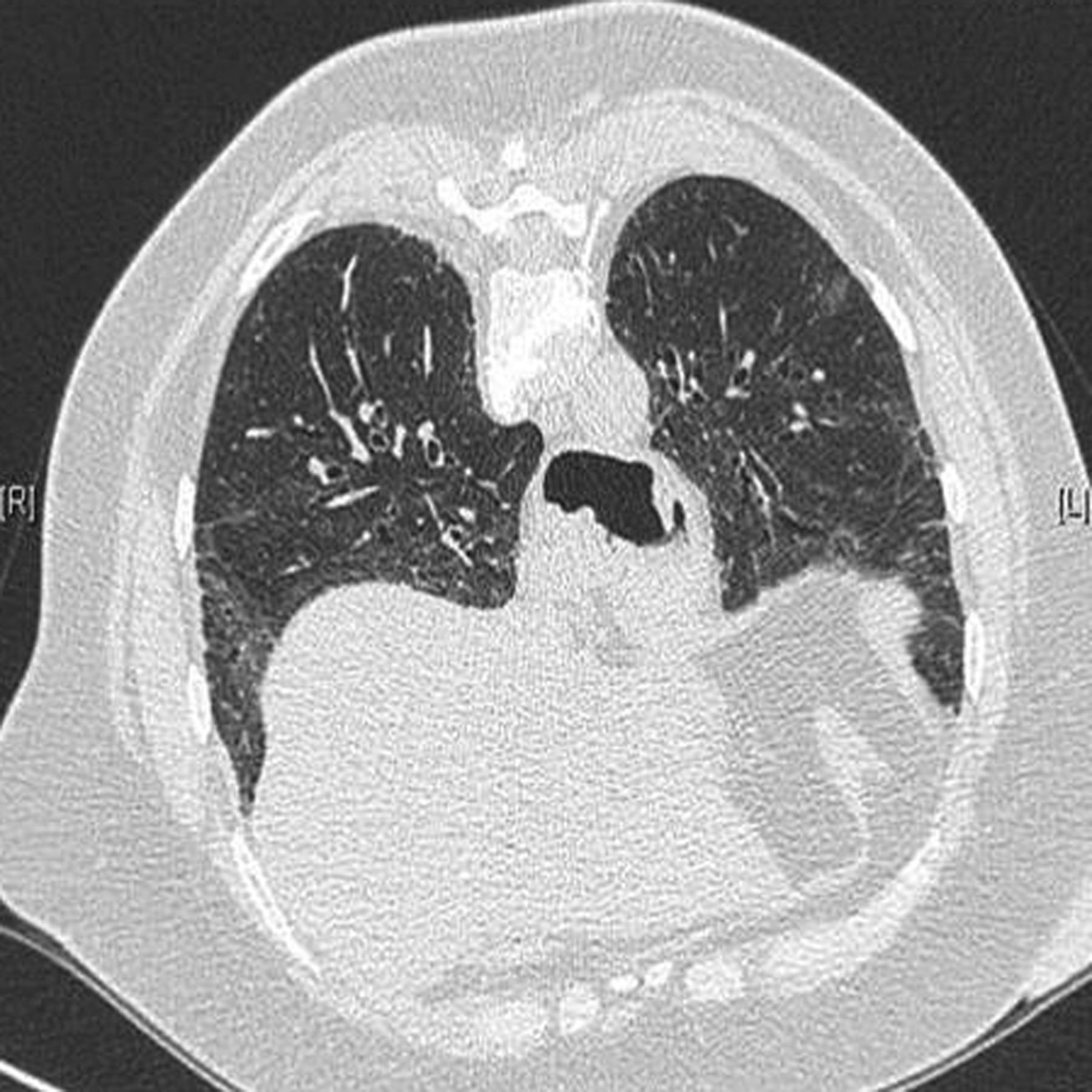
Irregular linear opacities in a fine reticular pattern by a combination of thickening of interlobular and intralobular septausually involves mainly the lower lung zones With the progression of disease reticular pattern becomes more coarse and diffuse and honeycombing may be seen most markedly near the diaphragm.
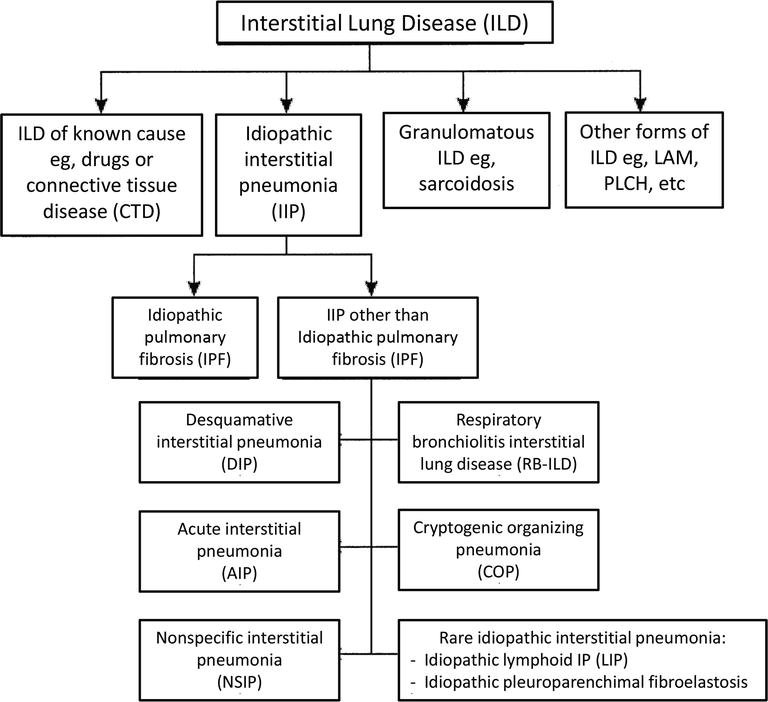
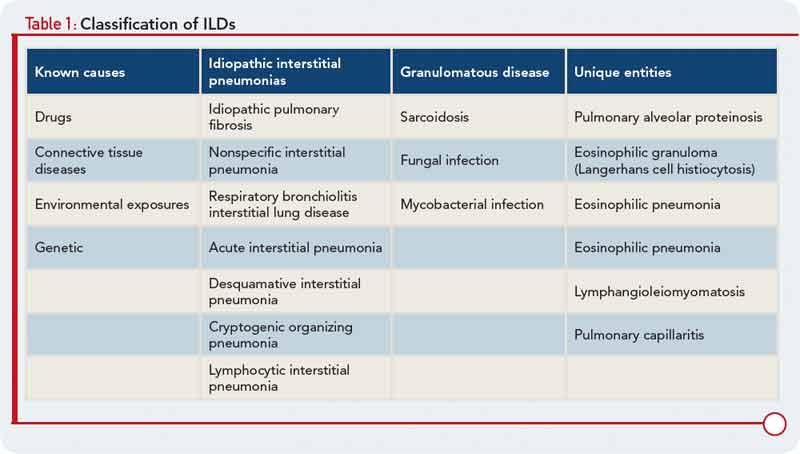
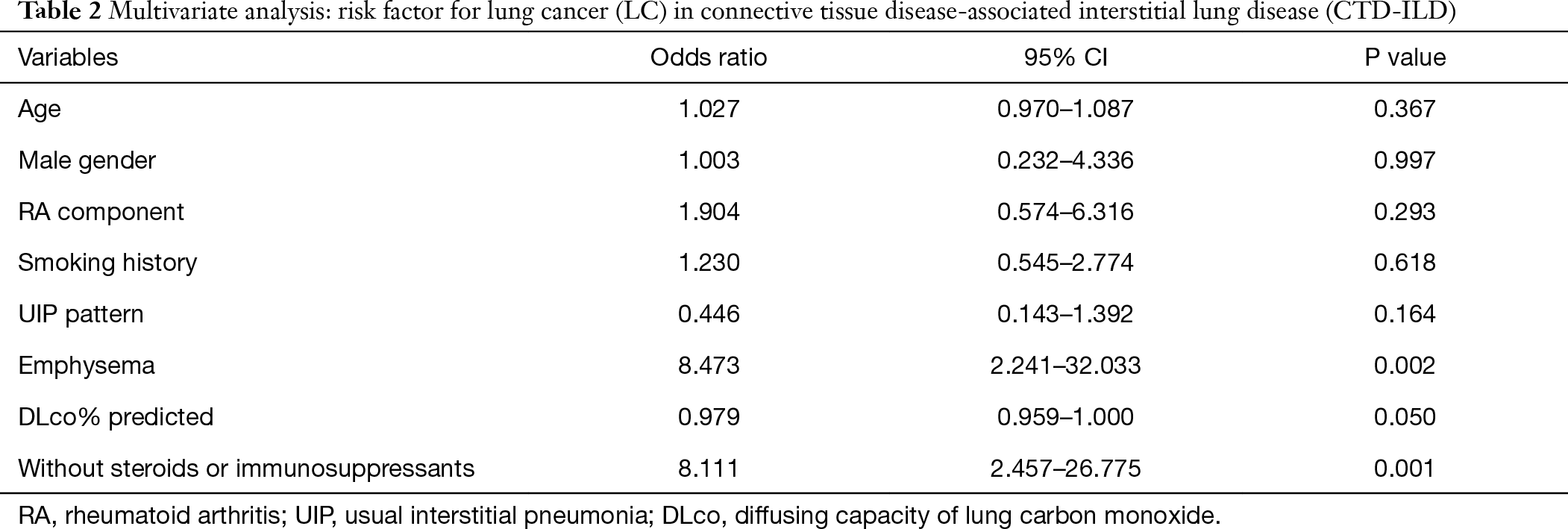
Effective therapies for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease CTD-ILD are still lacking. Connective tissue diseases CTDs cause a myriad of pulmonary complications including bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis pleuritis and pulmonary hypertension. On the other hand mixed connective tissue disease MCTD is a mixture or overlap of three different autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Early Stage. In their sera is an unusually high titer of a circulating antinuclear antibody with specificity for a nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigen. People with MCTD have symptoms and features of all three conditions either at the same time or over a period of time. Connective tissue diseases encompass a wide range of heterogeneous disorders characterised by immune-mediated chronic inflammation often leading to tissue damage collagen deposition and possible loss of function of the target organ. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common connective tissue diseases and can be inherited. It can have multiple manifestations.
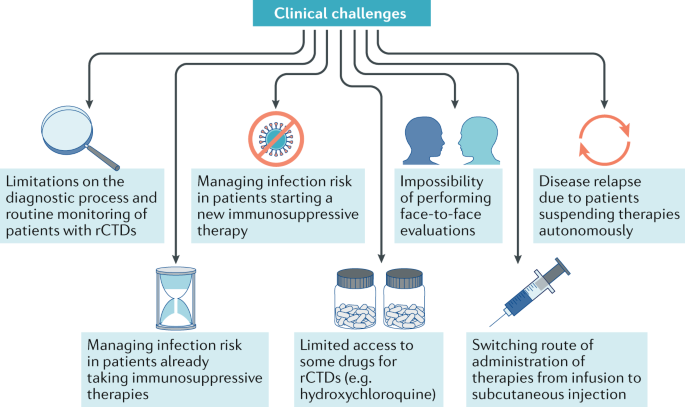
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Connective tissue diseases CTDs cause a myriad of pulmonary complications including bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis pleuritis and pulmonary hypertension. Early Stage. Lung involvement is a common complication of connective tissue diseases. In autoimmune disease the bodys immune system can attack its own organs causing inflammation and injury. Interstitial lung disease ILD is a common and serious form of pulmonary involvement characterized by various patterns of inflammation and fibrosis on high-resolution CT HRCT scan and in lung biopsy specimen. Connective tissue diseases encompass a wide range of heterogeneous disorders characterised by immune-mediated chronic inflammation often leading to tissue damage collagen deposition and possible loss of function of the target organ.






























Post a Comment for "Connective Tissue Disease Lungs"